The best way to organize JavaScript
Well-organized code can be easier to debug, and easier to revisit and change later. Writing organized code is a highly-valued skill in the programming field. When working on a team, you’ll often collaborate with other developers. Clean code is easier for others to understand and contribute to. Let’s make sure we understand how to organize our code using the best practices.
One of the most important organizational rules to follow is keeping what is known as your user interface and business logic separate.
User Interface and Business Logic
To help explain user interface and business logic let’s think about a calculator application. Its code falls into two categories:
- code that performs calculations
- code responsible for interacting with the user.
The code that handles the math is the business, or also known as the back-end logic. It’s the ‘inner workings’ of the application that performs calculations and returns a value. It’s what takes the numbers 8 and 2, adds them together, and get 10.
The code that handles interacting with a user is the user interface, or also known as the front-end logic. It retrieves information from the user and provides it to the business logic to calculate. While buttons on a calculator may be labeled with numbers, they’re just visual buttons. User interface logic is what translates clicking on this area of the page:
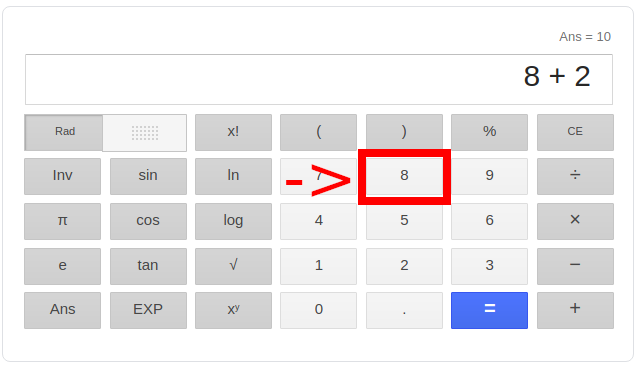
into the number 8. The user interface logic registers that the user has pushed the button labeled “8”. It then provides the number 8 to the business logic where we may perform calculations with it.
Let’s say we also press the buttons labeled “+” and “2” and “=”. The user interface logic also translates these interactions into the number 2 and recognizes it will need a function for addition. The business logic then adds the numbers 8 and 2 together, and returns 10. The user interface logic can then display this result to the user:
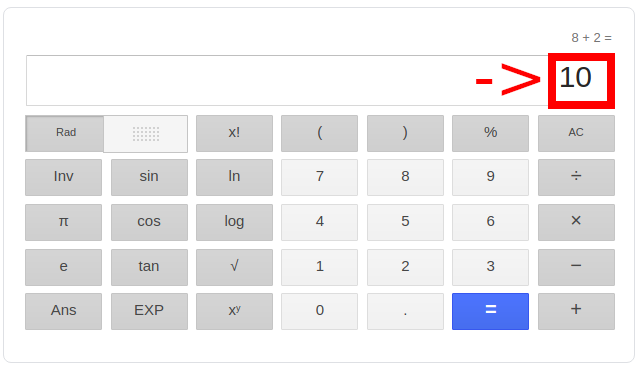
User interface logic handles interacting with the user; including displaying or gathering information. The business logic handles calculating or updating information ‘behind the scenes’.
Separation of Logic
Since user interface and business logics have separate purposes, their code should always be separate.
conclusion
The code that handles calculations is the business or back-end logic. It’s the ‘inner workings’ of the application that performs calculations and return a value. The code that handles interacting with a user is the user interface, or front-end logic. It retrieves information from the user and provides it to the business logic to calculate. Understanding the basic differences between these two logics, and knowing that they should be separate, you’ll know one of the best practices to organize JavaScript.

